Ovulation Dysfunction & Infertility
Ovulation dysfunction, also called ovulation disorders, is one of the most common causes of infertility in women and is due to issues with the release of a mature egg for potential fertilization during a woman’s menstrual cycle. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) reports that approximately 25% of all infertility problems are ovulation related.1
If you’re struggling to conceive, the fertility specialists at The Fertility Institute can help you determine if you’re experiencing ovulation dysfunction.
What is Ovulation Dysfunction?
A woman’s ovulation can be affected by the health of her ovaries and the endocrine system, which plays an essential role in her menstrual cycle.
During a normal menstrual cycle, the endocrine system prepares the body for pregnancy by secreting hormones, most notably gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Both promote egg maturity along with luteinizing hormone (LH) that causes the release of the egg, and progesterone that helps prepare the uterine lining for possible pregnancy.
A change in the production of these hormones or their delivery can diminish ovulation, leading to ovulation dysfunction. There are five primary types of ovulation disorders.
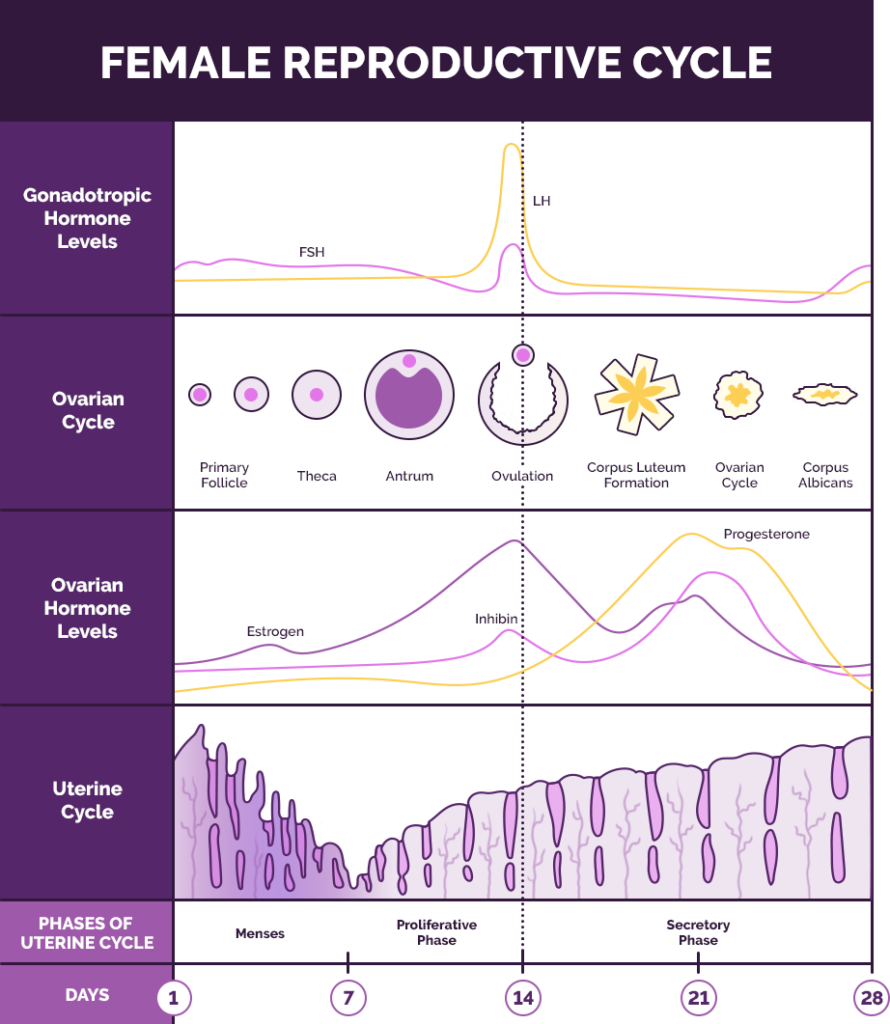
Hormone Imbalance
Hormones play a crucial role in female reproduction, specifically those hormones that control the menstrual cycle. If a woman’s reproductive system produces less than or more than the necessary amount of hormones for ovulation, this creates an improper balance.
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism and can affect overall bodily functions. Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone) and hyperthyroidism (too much), can negatively impact a woman’s hormone balance and fertility.
Hormone imbalance symptoms are:
- Fatigue
- Sleep problems
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Chronic acne
- Weight gain
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal imbalance that affects a woman’s insulin responsiveness, testosterone, and luteinizing hormone levels. It is the leading cause of infertility due to hormonal imbalance and a common ovulation dysfunction.
When a woman’s testosterone levels are elevated, she can experience irregular or absent periods or anovulation. This can prevent mature eggs from releasing and may turn into ovarian cysts. Over time, the production of multiple cysts can block ovarian follicles from producing mature eggs, while an imbalance of testosterone can disturb ovulation and cause infertility.
Polycystic ovary syndrome includes the following symptoms:
- Excessive hair on the face, chest, upper thigh and stomach
- Weight gain
- Severe acne and oily skin
- Male-pattern baldness or thinning hair
- Decrease in sexual desire, anxiety and depression
lEARN mORE
Hypothalamic Dysfunction
Hypothalamic dysfunction is when the hypothalamus, an area in the brain that manages the pituitary gland and regulates various bodily functions, is working improperly. It can cause an absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) due to the brain not properly signaling the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
At times, the hypothalamus will stop producing GnRH, which reduces the amount of other hormones produced (FSH, LH, and estrogen). This can ultimately lead to infertility. Symptoms include the following:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Hair loss
Hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is the excess production of prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that regulates milk production. This excess can reduce estrogen levels and disrupt ovulation, resulting in infertility.
Hyperprolactinemia can be caused by pregnancy and is most often related to a problem with the pituitary gland. It can occur due to a prolactin-secreting tumor (prolactinoma) or a large pituitary tumor that constricts the rest of the gland. The use of various medications can also cause hyperprolactinemia.
Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia include:
- No period or irregular periods
- Vaginal dryness
- Producing breast milk when not pregnant
Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), previously known as premature ovarian failure, is when a woman’s ovaries stop working before she enters menopause. When this occurs, menstrual cycles become irregular and eventually end.
As a result, the ovaries stop making hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone and she stops ovulating regularly, if at all. This leads to an early onset of menopause and infertility. Women between the ages of 35 and 40 are at a higher risk for premature ovarian insufficiency.
While the exact cause is unknown, genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases, radiation, or chemotherapy treatments have been linked to premature ovarian insufficiency.
Symptoms include:
- Trouble conceiving
- Hot flashes
- Vaginal dryness
- Irritability
- Decreased sex drive
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles
Diagnosing and Treating Ovulation Dysfunction
While each ovulation disorder is unique, many can be diagnosed with an examination or by reviewing menstrual and medical history. Diagnosing other disorders may require laboratory blood testing or an ultrasound to assess the ovaries. In the majority of cases, ovulation disorders can be treated with lifestyle changes or medication.
If you think you may be experiencing infertility due to ovulation dysfunction, speak to the fertility specialists at The Fertility Institute about your options.
Quick Links for
Female Infertility
- Ovulation Dysfunction & Infertility
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Recurrent Miscarriage (Pregnancy Loss)
- Uterine Fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Age & Fertility
- Secondary Infertility
- Tubal Ligation

Need Help with Financing Your Treatment Plan?
We provide various financing options to help make your reproductive journey as affordable as possible. Learn more about the resources available to you.
